Community food systems planning provides a systematic and comprehensive approach to identifying food system challenges and opportunities within a community and developing public policy tools to address them.
GFCUS
Community food systems planning provides a systematic and comprehensive approach to identifying food system challenges and opportunities within a community.
What is a Community Food System?
A food system is the soil-to-soil system that connects food production, processing, distribution, acquisition, consumption and waste disposal in food and agriculture. This includes all the resources, technologies, stakeholders, relationships, policies and laws that shape and influence how food moves through the system – from farm to plate and back to the farm again. In a well-functioning community food system, the food production, processing, distribution, consumption and post-consumer waste disposal are all integrated to enhance the environmental, economic, social and nutritional health of a particular place and its inhabitants.
Community Food Systems Planning
Community Food Systems Planning
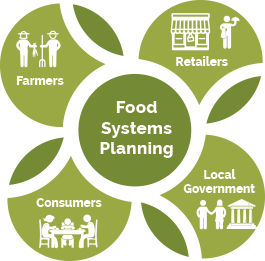
At its best, food systems planning is rooted in the collaborative partnership between the food system community, including farmers, retailers, and consumers, and the local and regional governments.
Food systems planning is a set of interconnected, forward-thinking activities that strengthen a community’s food system through the creation and implementation of plans and policies. Individuals and organizations engaged in food system planning identify the opportunities and challenges within communities’ food systems, gather input from stakeholders and deliberate on the actions best suited to respond to challenges, and facilitate and implement actions to strengthen food systems. At its best, food systems planning is rooted in the collaborative partnership between the food system community, including farmers, retailers and consumers, and the local and regional governments.
Through the food systems planning process, local and regional governments develop and implement a variety of public policies to influence and shape how food is produced, processed, distributed, accessed, purchased, consumed or disposed. These policies provide direction and guidance on how to address opportunities and challenges faced by the community’s food system. Examples of public policies that address food systems include:
- Comprehensive or other official plans that support food systems in their goals, objectives and implementation actions.
- Laws and ordinances that regulate different parts of the food system.
- Public education programs.
- Financial investments, through grants and tax incentives, to support different parts of the food system.
